This sexually-transmitted pox-virus causes small, benign skin tumors to grow on the vulva, which are usually symptomless, but annoying.
The tumors appear as dome-shaped lumps, 1-2 mm in diameter with tiny dimples in their center, and contain a white, cheese-like material.
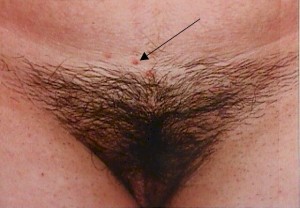
Treatment involves scraping off the lesion with a sharp dermal curette, and then coagulating the oozing base with Monsel’s solution or AgNO3 sticks and applying direct pressure. Cryosurgery is also effective, as is the application of trichloracetic or bichloracetic acid directly to the lesion (taking care not to disturb the surrounding normal skin.) Using local anesthetic, electrocautery may also be used.
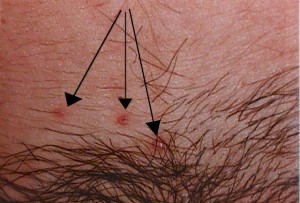
Left alone, they will generally resolve spontaneously after 6-12 months, but the patient remains contagious for as long as she has them.
