a. Abortion refers to the loss of the fetus before viability (twenty weeks gestation or fetal weight of 400 gr/14 oz) (see figure 1-7).
The types of abortion are:
(1) Spontaneous (miscarriage)-the process starts of its own accord through natural causes.
(2) Induced-intervention by outside source whether therapeutic or other reasons.
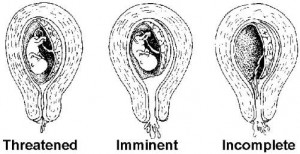
(3) Threatened-possible, but can be prevented. Bleeding or spotting occurs with the cervix closed. The patient may have mild cramps.
(4) Inevitable-the process has gone so far that loss of the fetus will occur, it cannot be prevented.
(5) Incomplete-parts of the products of conception have been passed, but part (usually the placenta) is retained in the uterus.
(6) Complete-all products (placenta and fetus) of pregnancy are eliminated.
NOTE: See figure 1-7 for some types of abortion.
[otw_is sidebar=otw-sidebar-1]
b. Nursing implications are listed below.
(1) Implement all nursing measures for a patient on complete bed rest.
(2) Monitor peri-pads for amount and character of vaginal bleeding.
(3) Be knowledgeable of local laws which support legal abortions.
(4) Refer questions of legal abortions to immediate supervisor so further counseling can be offered to the mother.
(5) Assess the mother’s emotional and spiritual needs.
