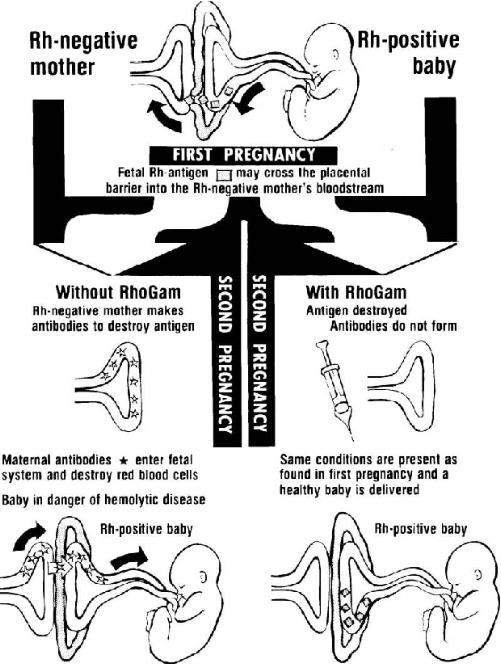
a. Rh incompatibility occurs when the Rh-negative pregnant patient carries an Rh-positive fetus.
The patient’s body reacts to the “foreign” fetus blood type. The mother produces antibodies that in-turn causes destruction of the fetus red blood cells (hemolysis). Hemolysis of the fetus red blood cells deprives the fetus of oxygen (erythroblastosis fetalis).
Brookside Note: This section was originally titled, “RhoGAM® INCOMPATIBILITY,” an obvious typographical error. It has been changed to what certainly was the original intent.
b. The treatment for Rh incompatability is given below.
(1) RhoGAM® (immune globulin) administered 72 hours following the birth of an Rh-positive child will eliminate maternal isoimmunization. Refer to figure 1-2.
(2) An Rh-negative patient whose sex partner is Rh-positive, who aborts or has an ectopic pregnancy, should receive RhoGAM®. This is essential to prevent the patient from developing Rh-positive antibodies.
c. Nursing implications are listed below.
(1) Follow the obstetrics (OB) practitioner’s or physician’s orders for drawing of Rh antibody titer.
(2) Follow delivery room standing operating procedure (SOP) to obtain cord blood sample to determine baby’s blood type.