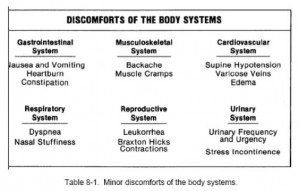
a. Nausea and Vomiting (Morning Sickness).
(1) One of the most common discomforts of early pregnancy is possibly due to high levels of humanchorionic gonadotropin (HCG) or progesterone, cultural expectations, emotional factors, and hypoglycemic reaction as a result of increased basal metabolism due to the 24-hour a day fetal and maternal body functions, especially after a period of fasting (from night to morning).
(2) Nausea and vomiting usually appear early in the first trimester (6 to 8 weeks) and subsides by the end of the 12th week of pregnancy.
(3) This is most bothersome in the morning when a woman awakes and the stomach is empty. Some pregnant women may experience this sort of discomfort at other times of the day.
(4) Nursing interventions consist of advising the mother to:
(a) Eat a high-protein snack at bedtime if it’s a hypoglycemic attack.
(b) Eat crackers or a piece of dry toast before getting up (keep by bedside if possible).
(c) Eat frequently spaced, small meals of high-quality (protein) foods.
(d) Sip a hot drink before arising.
b. Heartburn (Pyrosis).
(1) Heartburn is a burning sensation in the epigastric and sternal region. It results from relaxation of the cardiac sphincter and the decreased tone and mobility of smooth muscles which is due to increased progesterone thereby allowing for esophageal regurgitation, decreased emptying time of the stomach, and reverse peristalsis.
(2) Nursing interventions consist of advising the patient to:
(a) Eat frequent, small meals.
(b) Take sips of milk or hot tea.
(c) Eat slowly.
(d) Avoid fatty and gas-forming foods.
(e) Maintain good posture to give the gastrointestinal tract lots of space.
(f) Do not lie down after eating.
c. Constipation.
(1) The gastrointestinal tract motility is slowed due to increased progesterone resulting in increased reabsorption of water and drying of stool; and compression of the intestines by the enlarging uterus.
(2) Predisposition to constipation due to oral iron supplement (side effect of iron therapy is constipation). Some patients respond with diarrhea.
(3) Nursing intervention consists of advising the patient to:
(a) Drink at least six glasses of water per day.
(b) Increase roughage in the diet (for example, bran, coarse ground cereals, and fresh fruits and vegetables with skins).
(c) Do moderate exercise every day, especially walking.
(d) Maintain a regular schedule for bowel movements.
(e) Utilize deep breathing and relaxation techniques.