Menstruation is the periodic discharge of blood, mucus, and epithelial cells from the uterus.
It usually occurs at monthly intervals throughout the reproductive period, except during pregnancy and lactation, when it is usually suppressed.
a. The menstrual cycle is controlled by the cyclic activity of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and LH from the anterior pituitary and progesterone and estrogen from the ovaries. In other words, FSH acts upon the ovary to stimulate the maturation of a follicle, and during this development, the follicular cells secrete increasing amounts of estrogen (see figure 1-7).
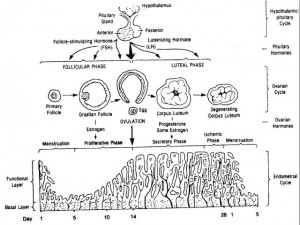
b. Hormonal interaction of the female cycle are as follows:
(1) Days 1-5. This is known as the menses phase. A lack of signal from a fertilized egg influences the drop in estrogen and progesterone production. A drop in progesterone results in the sloughing off of the thick endometrial lining which is the menstrual flow. This occurs for 3 to 5 days.
(2) Days 6-14. This is known as the proliferative phase. A drop in progesterone and estrogen stimulates the release of FSH from the anterior pituitary. FSH stimulates the maturation of an ovum with graafian follicle. Near the end of this phase, the release of LH increases causing a sudden burst like release of the ovum, which is known as ovulation.
(3) Days 15-28. This is known as the secretory phase. High levels of LH cause the empty graafian follicle to develop into the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum releases progesterone, which increases the endometrial blood supply. Endometrial arrival of the fertilized egg. If the egg is fertilized, the embryo produces human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). Thehuman chorionic gonadotropin signals the corpus luteum to continue to supply progesterone to maintain the uterine lining. Continuous levels of progesterone prevent the release of FSH and ovulation ceases.
c. Additional Information.
(1) The length of the menstrual cycle is highly variable. It may be as short as 21 days or as long as 39 days.
(2) Only one interval is fairly constant in all females, the time from ovulation to the beginning of menses, which is almost always 14-15 days.
(3) The menstrual cycle usually ends when or before a woman reaches her fifties. This is known as menopause.
