This is the Archived Desktop Edition.
You should be transferred to the Newest Edition for Desktop and Mobile within 2 seconds.
|
Lesson 2: Embryology and Fetal Development
2-13. PRINCIPLES OF FETAL IMMUNOLOGY
a. During the third trimester, passive immunity to some diseases is provided by the mother.
b. Diseases that the fetus receives temporary protection from include:
(1) Rubella.
(2) Diphtheria.
(3) Measles.
(4) Poliomyelitis.
(5) Tetanus.
(6) Mumps.
c. Passive immunity is short term and infants must begin immunization against the above diseases by the age of 2 months.
a. Multi-fetal pregnancy is a pregnancy involving two or more fetuses.
b. Twin fetuses may originate several ways (see figure 2-11).
(1) Identical twins (monozygotic) originate from the same ovum and are always of the same sex. They share a single placenta.
(2) Fraternal twins (dizygotic) originates from two separate ova and sperm and may be of different sexes. They each have their own placenta.
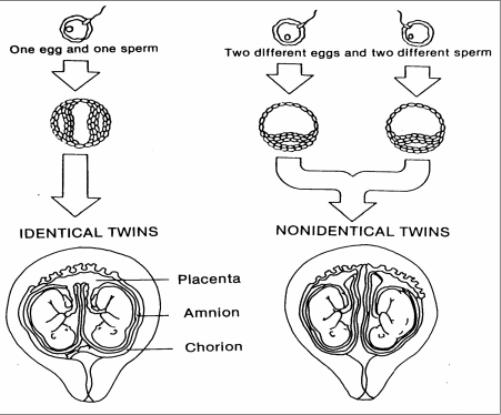
Figure 2-11. Development
of twin fetuses.
c. Pregnancies involving more than two fetuses (that is, triplets, quadruplets) may occur by either situation.
(1) Monozygotic--all will be identical.
(2) Multi-zygotic--often associated with fertility drugs in which the ovary matured and released many eggs in the same cycle.
In closing, a working knowledge of the development of the human baby from conception to birth is essential for you to function effectively as a practical nurse. The information covered in this lesson, along with Lesson 1, will help you in carrying out the nursing process in labor and delivery, and caring for the newborn infant.
|
The Brookside Associates Medical Education Division is dedicated to the development and dissemination of medical information that may be useful to medical professionals and those in training to become medical professionals. This website is privately-held and not connected to any governmental agency. The views expressed here are those of the authors, and unless otherwise noted, do not necessarily reflect the views of the Brookside Associates, Ltd., any governmental or private organizations. All writings, discussions, and publications on this website are unclassified.
© 2007 Medical Education Division, Brookside Associates, Ltd. All rights reserved