EXERCISES, LESSON 1
INSTRUCTIONS: Answer the following exercises by marking the lettered response that best answers the question, by completing the incomplete statement, or by writing the answer in the space provided.
After you have completed all of these exercises, turn to “Solutions to Exercises” at the end of the page and check your answers. For each exercise answered incorrectly, reread the material referenced with the solution.
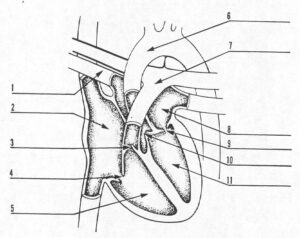
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR EXERCISES 1 THROUGH11. Exercises 1-11 should be answered by filling in the blanks to identify the heart structures in the figure below.
12. The two fluid transportation systems of the circulatory system are the ________________________ and the __________________________.
13. The chambers of the heart are lined with ________________________.
14. Blood from the upper part of the body enters the heart through a blood vessel called the ___________________________.
15. Blood flows from the right ventricle into the ________________________.
16. Systemic circulation starts from the _________________________, and the pulmonary circulation starts from the ______________________________.
17. The heart gets its blood supply from the _________________________.
18. The wave of expansion and recoil of an artery associated with the heartbeat is called the ______________________.
19. Cardiac fluoroscopy is used to show the heart in ___________________.
20. The procedure in which a radiopaque catheter is manipulated through the heart is called ______________________.
21. The graphic recording of the electrical impulses produced by the heart is called an _________________________.
22. The five major waves of the ECG are: _____, _____, _____, _____, and _____
23. Which ECG wave represents atrial depolarization?
a. T
b. P
c. R
d. Q
24. Which ECG wave represents electrical recovery of the ventricles?
a. P
b. R
c. T
d. S
25. The chest lead that is placed over the 5th intercostal space at the midclavicular line is the ______________________
26. The difference between the apical and radial pulse is called the ___________________________.
27. _____________________________ is the force or strength of the pulse.
28. List three terms used to describe the volume or force of a pulse.
___________________________________
___________________________________
___________________________________
29. Which of the following is NOT a factor that may affect pulse rate?
a. Body temperature.
b. Blood pressure.
c. Digestion.
d. Pain.
e. None of the above.
30. The pressure that occurs during contraction of the ventricles is called ___________________
31. Fear, anger, or anxiety will cause blood pressure to _________________.
32. The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures is called the ________________________________
33. The condition in which the coronary arteries cannot deliver adequate food supply to the heart is referred to as ________________________________.
34. Which of the following is NOT a modifiable risk factor?
a. Cigarette smoking.
b. Weight.
c. Sex.
d. Stress.
35. _______________________ is the most common form of arteriosclerosis.
36. A clinical syndrome of ischemic heart disease, in which pain occurs in the chest or adjacent areas, is called _________________________________
37. The pain of angina usually occurs during __________________ and is relieved with ______________________.
38. A non-transmural myocardial infarction involves_______________________ _____________________________
39. _______________________ is the greatest threat to life in the first hours after a myocardial infarction.
40. The clinical condition in which inadequate cardiac output results in poor perfusion of organ system is called____________________________
41. When increased pressure in the pulmonary vessels causes fluid to leak into the interstitial lung tissue, ______________________________ occurs.
42. The condition manifested by neck vein distention and body edema is called ___________________________
43. Hypertension that has no identifiable cause is referred to as _________________ hypertension.
44. For a cardiovascular surgical patient, poor ________________________ result in increased anxiety, which leads to a slower recovery.
45. Cramping pain in the calf and the appearance of swelling or redness along a vein are signs of ________________________________.
46. Compression of the heart from fluid accumulation in the pericardial sac is called __________________________________.
47. Why is it essential for paraprofessional nursing staff to be familiar with the layout of a crash cart? _________________________.
48. What does the recorder do during a “code?” ___________________________.
49. Sudden, sharp, stabbing chest pain and violent coughing in a post-operative CV surgical patient may indicate the present of _________________________.
50. Right sided heart failure without left sided failure is called _________________.
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES, LESSON 1
1. Pulmonary vein (Figure 1-2)
2. Right atrium. (Figure 1-2)
3. Pulmonary valve. (Figure 1-2)
4. Tricuspid valve. (Figure 1-2)
5. Right ventricle . (Figure 1-2)
6. Aorta. (Figure 1-2)
7. Pulmonary artery. (Figure 1-2)
8. Left atrium. (Figure 1-2)
9. Mitral valve. (Figure 1-2)
10. Aortic valve. (Figure 1-2)
11. Left ventricle. (Figure 1-2)
12. Cardiovascular system, lymphatic system. (para 1-1a, b)
13. Endocardium or endocardial tissue . (para 1-2d)
14. Superior vena cava. (para 1-3)
15. Pulmonary artery. (para 1-3b)
16. Left ventricle; right ventricle. (para 1-3e)
17. Coronary arteries. (para 1-4a)
18. Pulse. (para 1-6a)
19. In action (or motion). (para 1-12)
20. Cardiac catheterization. (para 1-15 b)
21. Electrocardiogram. (para 1-16a)
22. P, Q, R, S, T. (para 1-16b)
23. b. (para 1-16b)
24. c. (para 1-16b)
25. V4 lead. (para 1-16e)
26. Pulse deficit. para 1-19c)
27. Pulse volume. (para 1-19d)
28. Weak, thready, feeble, bounding, full, or strong. (para 1-19d)
29. e. (para 1-19e)
30. Systolic (or systole). (para 1-20b)
31. Increase (rise). (para 1-20d)
32. Pulse pressure. (para 1-20g)
33. CAD (coronary artery disease). (para 1-21)
34. c. (para 1-22a)
35. Atherosclerosis. (para 1-23b)
36. Angina pectoris. (para 1-25a)
37. Exertion; rest. para 1-25c)
38. Only partial thickness of the myocardial muscle. (para 1-26b)
39. Ventricular fibrillation. (para 1-26d)
40. Heart failure. (para 1-27a)
41. Pulmonary edema. (para 1-27b)
42. Congestive heart failure. (para 1-27c)
43. Primary or essential. (para 1-29b)
44. Coping mechanisms. (para 1-32b(5))
45. Thrombophlebitis. (para 1-35a)
46. Cardiac tamponade. (para 1-38)
47. To save time in an emergency. (para 1-42c)
48. Chart the exact time of each drug given and each procedure performed. (para 1-43c)
49. Embolism. (para 1-36a)
50. Corpulmonale. (para 1-27d)
