|
|
Operational Obstetrics & Gynecology
Labor and Delivery
Cervical Dilatation and Effacement
Using sterile gloves and lubricant, perform a vaginal exam and determine the dilatation and effacement of the cervix. A small amount of bleeding during the days or hours leading up to the onset of labor is common and called "bloody show."
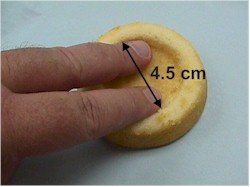
Dilatation is expressed in centimeters. I have relatively large fingers, and for my hands, I make the following generalizations:
-
1.5 cm: One finger fits tightly through the cervix and touches the fetal head.
-
2.0 cm: One finger fits loosely inside the cervix, but I can't fit two fingers in.
-
3.0 cm: Two fingers fit tightly inside the cervix.
-
4.0 cm: Two fingers fit loosely inside the cervix.
-
6.0 cm: There is still 2 cm of cervix still palpable on both sides of the cervix.
-
8.0 cm: There is only 1 cm of cervix still palpable on both sides of the cervix.
-
9.0 cm: Not even 1 cm of cervix is left laterally, or there is only an anterior lip of cervix.
-
10.0 cm: I can't feel any cervix anywhere around the fetal head.
Effacement is easiest to measure in terms of centimeters of thickness, ie., 1 cm thick, 1.5 cm thick, etc. Alternatively, you may express the thickness in percent of an uneffaced cervix...ie, 50%, 90%, etc. This expression presumes a good knowledge of what an uneffaced cervix should feel like.
Home · Introduction · Medical Support of Women in Field Environments · The Prisoner of War Experience · Routine Care · Pap Smears · Human Papilloma Virus · Contraception · Birth Control Pills · Vulvar Disease · Vaginal Discharge · Abnormal Bleeding · Menstrual Problems · Abdominal Pain · Urination Problems · Menopause · Breast Problems · Sexual Assault · Normal Pregnancy · Abnormal Pregnancy · Normal Labor and Delivery · Problems During Labor and Delivery · Care of the Newborn
|
Bureau of Medicine
and Surgery |
Operational
Obstetrics & Gynecology - 2nd Edition |
This web version of Operational Obstetrics & Gynecology is provided by The Brookside Associates Medical Education Division. It contains original contents from the official US Navy NAVMEDPUB 6300-2C, but has been reformatted for web access and includes advertising and links that were not present in the original version. This web version has not been approved by the Department of the Navy or the Department of Defense. The presence of any advertising on these pages does not constitute an endorsement of that product or service by either the Department of Defense or the Brookside Associates. The Brookside Associates is a private organization, not affiliated with the United States Department of Defense. All material in this version is unclassified.
This formatting © 2006
Medical Education Division,
Brookside Associates, Ltd.
All rights reserved