HCG is a hormone, produced by
placental tissue.
- Shortly after implantation of a fertilized ovum in the uterine
lining, HCG begins to be produced.
- Levels of HCG approximately double every 2-3 days in a normal
pregnancy.
- By the time of the first missed menstrual period, pregnancy tests
are usually positive (with a sensitivity of 30-35 mIU/ml).
- Following a miscarriage, HCG levels initially fall quickly, then
more gradually, until levels return to normal. This process takes, on
average, about a month.
Urine is normally used for the test. A morning urine is more sensitive
(in borderline situations) because it is more concentrated.
Serum can be used, and is equally reliable.
Elevations caused by:
- Pregnancy
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
Decreases caused by:
- Miscarriage (spontaneous or induced)
- Following obstetrical delivery
- With resolution of an ectopic pregnancy
|
Normal Values:
| |
mIU/ml |
|
Non-pregnant |
Negative |
|
Pregnant |
Positive |
More
information on Pregnancy Tests
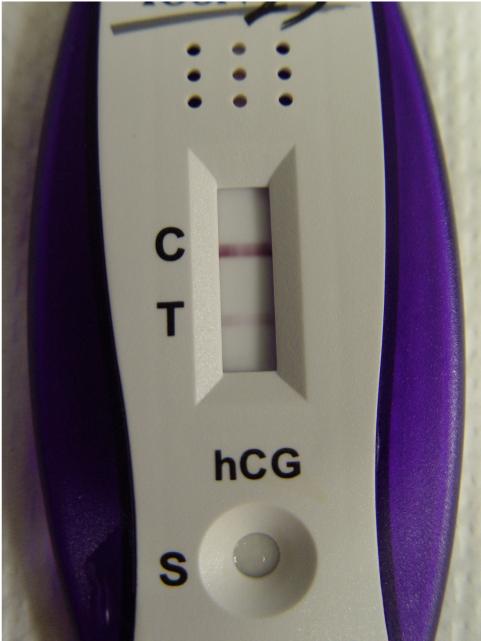
Positive Pregnancy Test
|
Source:
Operational Medicine 2001, Health
Care in Military Settings, NAVMED P-5139, May 1, 2001, Bureau
of Medicine and Surgery, Department
of the Navy, 2300 E Street NW, Washington, D.C., 20372-5300
OB-GYN 101:
Introductory Obstetrics & Gynecology
© 2003, 2004, 2005, 2008
Brookside Associates, LLC
All rights reserved
Other Brookside Products |