|
Wet Mount
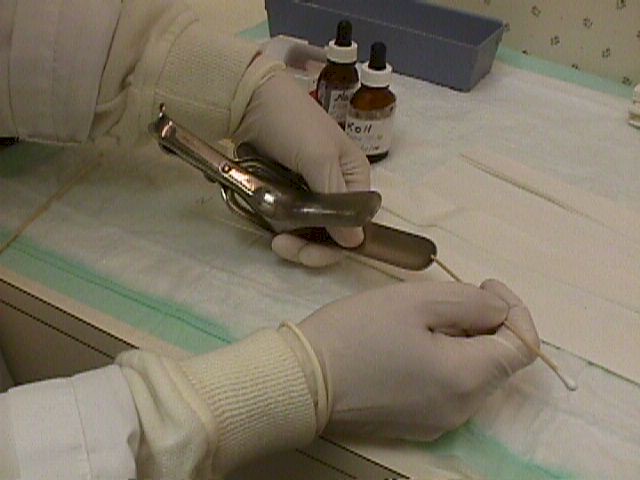
Use a wooden spatula or cotton-tipped applicator to directly obtain a
sample of the discharge.

If you start off with too much discharge, it will make it harder for you
to see the individual structures you need to evaluate.
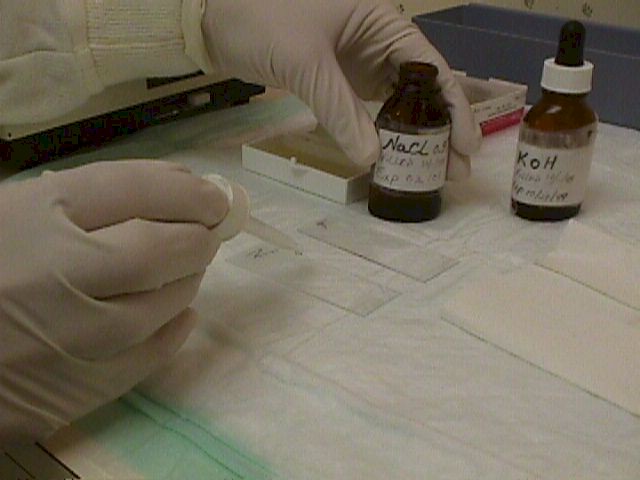
Add one drop of Normal Saline (0.9 percent NaCl) to the drop of discharge.
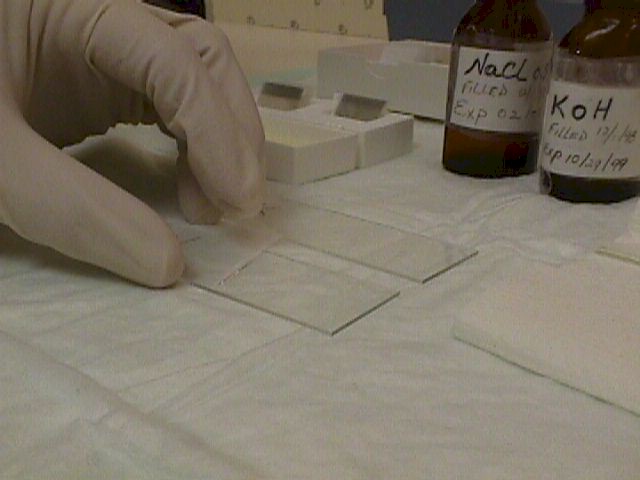
Place glass coverslips over the glass slides. Remove any excess fluid with tissue
paper.
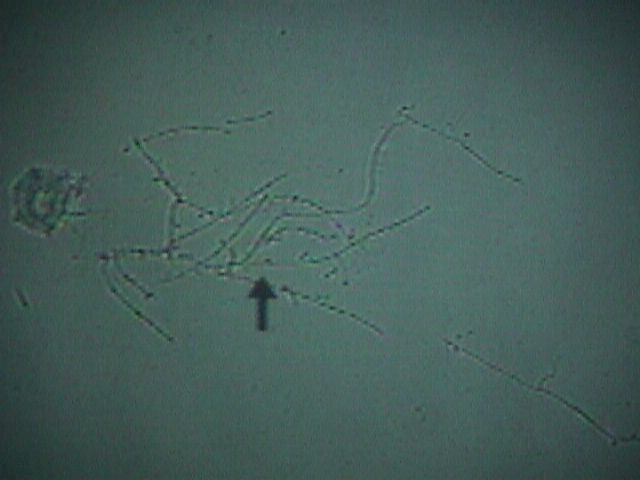
After the cell membranes are dissolved, the typical branching and budding
yeast cells can be seen.
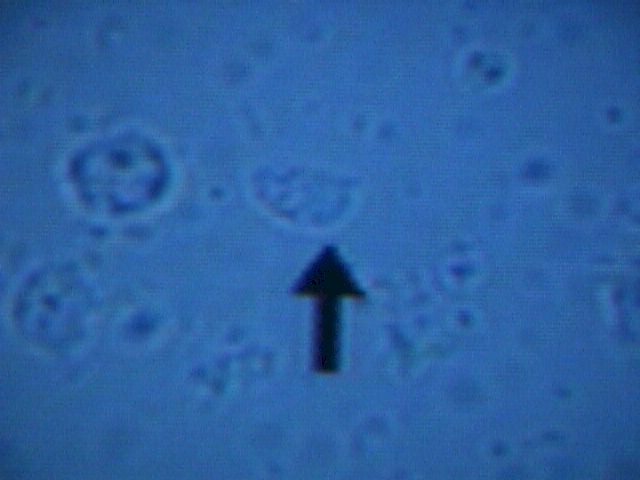
Trichomonas is best seen on the Normal Saline slide.
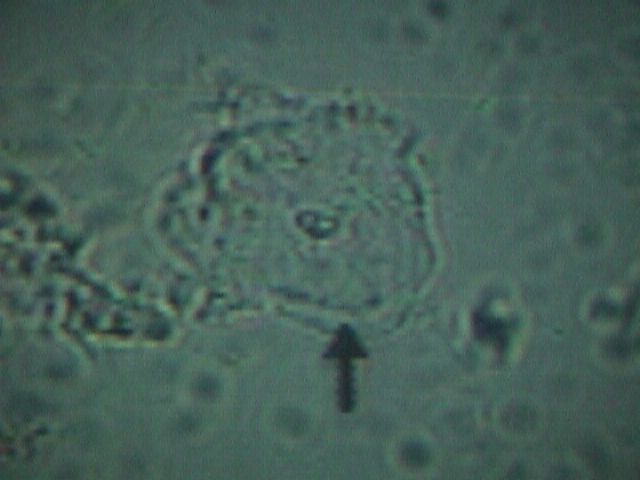
Normal Vaginal Epithelial Cell
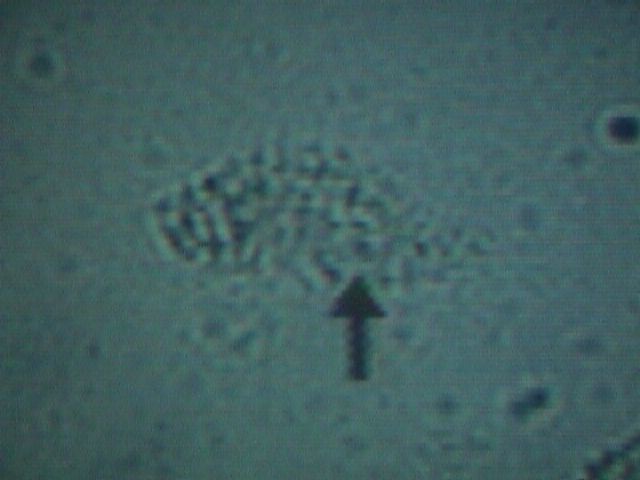
Clue Cell |
While it is often possible to correctly guess the cause of a vaginal
discharge, based on history and/or physical exam, it is sometimes useful to use laboratory
skills to confirm a clinical impression.
Obtain a Specimen
Use a wooden spatula or cotton-tipped applicator to directly
obtain a sample of the discharge. You can find abundant discharge on the inside
curve of the speculum after you remove it. It should be relatively fresh, but
processing can wait until you have completed the rest of your examination of the
patient. Note the color, consistency, odor (if any), and then set the specimen
aside.
Put a Tiny Amount of Discharge on a Microscope
Slide
Make this as small as possible. Later, when you view it under the microscope, it will
be spread as thin as a single cell. If you start off with too much discharge, it will make
it harder for you to see the individual structures you need to evaluate.
Some physicians use a single microscope slide for both the KOH
and NaCl preparation. Others prefer separate slides for each. Either method is
acceptable and a matter of personal preference.
Don't place the discharge on the glass slide until you are ready
to process it, or it can dry out. Drying out won't effect your ability to see
yeast organisms, but can significantly impair your ability to see movement from
trichomonas.
Add NaCl and KOH
Add one drop of Normal Saline (0.9 percent NaCl) to the drop of discharge. Mix well on
the slide. This is the slide you will use for identifying Trichomonas and bacterial
vaginosis (BV).
Prepare a second slide in the same way, using 10 percent Potassium Hydroxide (KOH).
This is the slide you will use to identify yeast.
Some people find it convenient to use only a single slide, with KOH at one end and NaCl
at the other end
Add Coverslips
Place glass coverslips over the glass slides. Remove any excess fluid with tissue
paper.
In order for the KOH to be effective in dissolving the cell membranes of everything
except yeast, you need to allow some time. A minute or two may be enough.
If you are in a hurry, you can speed the process by heating the slide with a match or
lighter. The elevated temperatures will speed the dissolving process and the glass slide
cools quickly enough that you can place it under the microscope as soon as you've finished
heating it.
Microscopic Evaluation
Examine the prepared slides under a microscope.
Experienced practitioners often find the lowest power (about 40X) works the best.
Others will start at low power and then move to slightly higher power (about 100X).
The magnification is determined by multiplying the power of the eyepiece (typically
10X) by the power of the objective lens (4X, 10X, 40X, 80X) to get the various possible
total magnifications (40X, 100X, 400X, and 800X in this example.)
Yeast
Yeast (Candida, Monilia) is best identified with the KOH slide.
After the cell membranes are dissolved, the typical branching and budding yeast cells
can be seen. Sometimes, it has the appearance of a tangled web of threads. At other times,
only small branches will be seen.
Yeast normally live in the vagina, but only in very small numbers. If you visualize any
yeast in your sample, it is considered significant.
Read more about yeast
Trichomonas
Trichomonas is best seen on the Normal Saline slide.
These protozoans are about the same size as a white blood cell (a little smaller than a
vaginal epithelial cell), but their violent motion is striking and unmistakable.
Read more about trichomonads
Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis (also known as Gardnerella, hemophilus, or
non-specific vaginitis) is characterized by the presence of "clue cells"
visible at both low and medium power.
These clue cells are vaginal epithelial cells studded with bacteria.
It resembles a pancake that has fallen into a bowl of poppy seeds, but
on a microscopic level.
A normal vaginal epithelial cell is clear, with recognizable
contents, and sharp, distinct cell borders.
A clue cell appears smudged, with indistinct contents and fuzzy,
poorly defined borders.
Read more about
Bacterial Vaginosis
|








