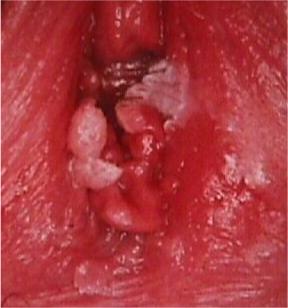
Condyloma
|
Once a patient has had condylomata, the
skin always sheds virus to some degree. As such, barrier
contraception (e.g. condoms) is recommended unless a couple is
actually trying to conceive. The question of who gave the virus to
whom is not a useful one. The virus may have been shed
asymptomatically by either partner for quite some time before lesions
develop. The goal is to make your patient
free of visible warts for as long as possible. Eradication of the
virus from the skin is impossible. Destructive modalities delivered
with precision such as liquid nitrogen, Trichloroacetic acid,
electrosurgery, and podophyllin are helpful. Podophyllin resin in tincture of
benzoin has long been a mainstay of therapy. Apply it to external
lesions (do not apply to vaginal or cervical warts in women or use
during pregnancy) and wash off with soap and water after 4 - 6 hours.
Re-evaluate your patient 1 week after treatment to determine whether
additional therapy is necessary. A new form of podophyllin (Condylox)
is commercially available and should only be considered for
emotionally mature, dexterous, and reliable patients. The active
ingredient is podofilox, a purified and standardized form of
podophyllin toxin suitable for self-application by a patient. Podofilox is meant only for
external condylomata and should not be used on mucous membrane lesions
or during pregnancy in females. Follow the PDR recommendations
carefully because over treatment will result in considerable
irritation. This should be applied only to lesional skin. This
medication is also quite expensive. It is not meant for everyone. Other pharmacologic means to
treat condylomata include biologic response modifiers such as topical
imiquimod cream (Aldara) and intralesional interferon. These
modalities are very costly and are only considered appropriate for
treatment when prescribed by Dermatologists. |
Written and revised by CAPT Dennis A. Vidmar, MC, USN, Department of Military and Emergency Medicine, and Department of Dermatology, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, Bethesda, MD (1999). Additional images provided by CAPT Vidmar in June, 2000, subsequent to the initial publication of this manual. |
Preface · Administrative Section · Clinical Section
The
General Medical Officer Manual , NAVMEDPUB 5134, January 1, 2000
Bureau
of Medicine and Surgery, Department of the Navy, 2300 E Street NW, Washington, D.C.,
20372-5300
This web version of The General Medical Officer Manual, NAVMEDPUB 5134 is provided by The Brookside Associates Medical Education Division. It contains original contents from the official US Navy version, but has been reformatted for web access and includes advertising and links that were not present in the original version. This web version has not been approved by the Department of the Navy or the Department of Defense. The presence of any advertising on these pages does not constitute an endorsement of that product or service by either the Department of Defense or the Brookside Associates. The Brookside Associates is a private organization, not affiliated with the United States Department of Defense. All material in this version is unclassified. This formatting © 2006 Medical Education Division, Brookside Associates, Ltd. All rights reserved.
Home · Textbooks and Manuals · Videos · Lectures · Distance Learning · Training · Operational Safety · Search
|
|
|
This website is dedicated to the development and dissemination of medical information that may be useful to those who practice Operational Medicine. This website is privately-held and not connected to any governmental agency. The views expressed here are those of the authors, and unless otherwise noted, do not necessarily reflect the views of
the Brookside Associates, Ltd., any governmental or private organizations. All writings, discussions, and publications on this website are unclassified.
© 2006 Medical Education Division, Brookside Associates, Ltd. All rights reserved
Other Brookside Products