CORRESPONDENCE COURSE
U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL
SUBCOURSE MD0904 EDITION 100

One of the 91WM6’s most important responsibilities is the safe administration of medication. Used intelligently and accurately, drugs can surely save countless numbers of lives; used unwisely, they can have disastrous results.
It is imperative that you have a thorough understanding of the basic concepts of math as well as the specific mathematical skills required for pharmaceutical calculations.
———————-
Download Here
Pharmacology Math for the Practical Nurse
Length: 167 Pages
Estimated Hours to Complete: 12
Format: PDF file
Size: 2.8 MB
—————————-
Anyone may take this course. However, to receive credit hours, you must be officially enrolled and complete an examination furnished by the Nonresident Instruction Branch at Fort Sam Houston, Texas. Enrollment is normally limited to Department of Defense personnel. Others may apply for enrollment, but acceptance is not guaranteed.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
PRETEST FOR LESSON 1
Pretest Answer Sheet
1 BASIC MATH
Section I. Basic Arithmetic
Section II. Fractions
Section III. Decimals
Section IV. Percentages
Section V. Ratio and Proportion
Exercises
2 PHARMACOLOGY
Section I. Ratio and Proportion Operations
Section II. Systems of Measurement
Section III. Computing Medication Dosages
Section IV. Computing Intravenous Infusion Rates
Section V. Basic Dose Calculations
Exercises
Sample
LESSON ASSIGNMENT
LESSON 1 Basic Math.
TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 1-1 through 1-57.
LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
1-1. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers.
1-2. Reduce fractions to lowest terms.
1-3. Change improper fractions to mixed numbers or whole numbers and mixed numbers to improper fractions.
1-4. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide fractions and mixed numbers.
1-5. Add, subtract, divide, and multiply decimals.
1-6. Change decimals to fractions and fractions to decimals.
1-7. Solve problems using the ratio and proportion method.
SUGGESTION After completing the assignment, complete the exercises at the end of this lesson. These exercises will help you to achieve the lesson objectives.
LESSON 1
BASIC MATH
Section I. Basic Arithmetic
1-1. GENERAL
a. Whole Numbers. The number zero and the counting numbers (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, …) are whole numbers. The first 10 whole numbers (0 through 9) are called digits.
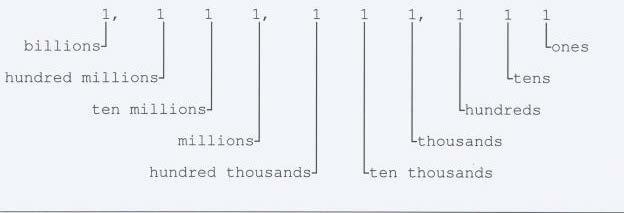
b. Powers of Ten. Our number system is based upon the powers of ten. That is, the digit place to the immediate left of a given digit is worth ten times as much as the given digit place, and the digit place to the immediate right is worth one-tenth as much. For example, in the number 321, the one tells you how many ones (or units) are in the number, the two tells how many tens, and the three tells how many hundreds. See figure 1-1.
Figure 1-1. The number system.1-2. SIMPLE ADDITION
a. The numbers to be added are the addends. The answer to an addition problem is the sum. When you are doing a problem in addition, work from right to left. Be sure to keep the columns of numbers in straight lines.
b. When you “carry” a number over to the next column to the left, you can jot it down at the top of the column.
EXAMPLE: Find the sum of 263, 19, and 1202.