EXERCISES, LESSON 2
INSTRUCTIONS. Answer the following exercises marking the lettered response that best answers the question or best completes the incomplete statement, or by writing the answer in the space provided.
After you have completed all of these exercises, turn to “Solutions to Exercises,” at the end of the lesson and check your answers. For each exercise answered incorrectly, reread the material referenced with the solution.
1. For which one of the following reasons is a palliative surgical procedure done?
a. Remove a diseased organ.
b. Repair a body part.
c. Cure a disease.
d. Relieve pain.
2. A suffix used to denote an operation classified as an incision is which of the following?
a. centesis.
b. exeresis.
c. scopy.
d. desis.
3. A patient is scheduled to have a colpopexy performed. What is the operative procedure to be done?
a. Suspension of the colon.
b. Suturing of the scrotum.
c. Incision into the bladder.
d. Fixation of the vagina.
4. Which of the following actions would be helpful to a bereaved person?
a. Making decisions for him.
b. Helping him to feel like a valuable person.
c. Giving him a sedative so that he does not have to deal with his feelings.
d. Helping him to see that his grief serves no purpose.
5. After the doctor and hospital personnel have obviously done all that is possible to help Mr. Jones, he dies. His spouse is very angry with the doctor and threatens to sue. For what reason do you think Mrs. Jones is reacting in this manner?
a. She is dealing well his her feelings toward her husband.
b. She had neither positive nor negative feelings toward her husband.
c. She and her husband had unresolved anger in their relationship.
d. She feels in control of the situation.
6. What information is found on an instrument card in addition to the instruments needed for an operation?
a. Sutures needed.
b. Number of sterile gowns needed.
c. Number of straight tools needed.
d. Items such as sterile drains needed.
7. When the specialist desires a specific time off duty and no emergency exists, he should do which of the following?
a. Ask for the time off after the schedule is prepared.
b. Ask for the time off when the schedule is prepared, but before it is posted.
c. Write the request before the schedule is prepared.
d. Write the request when the schedule is prepared, but before it is posted.
FOR EXERCISES 8 AND 9. Use the following situation:
SITUATION: Your assignment for the day is to scrub for surgery.
8. Which of the following is the most appropriate source for learning detailed information concerning the performance of your assigned tasks as an OR specialist?
a. Noncommisioned officer in charge.
b. Operating room supervisor.
c. Nursing Service Assignment Roster.
d. Standing operation procedures.
e. Operating Room Schedule.
9. Which of the following sources should be used to identify the operations to which you are assigned?
a. Operating Room Schedule.
b. Nursing Service Assignment Roster.
c. Standing operation procedures.
d. Non commisioned officer in charge.
e. Operating room supervisor.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR EXERCISES 10 — 25. These exercises are based on the facsimile of the OR Schedule found below.
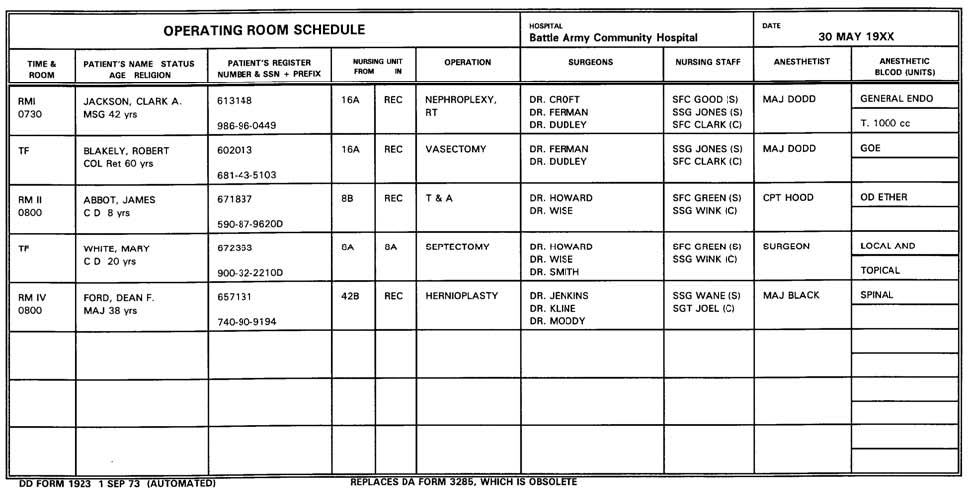
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR EXERCISES 10–20. Ten through 20 are based on the first operation listed.
10. “Rm 1” pertains to the:
a. Patient’s room number.
b. Room to which the patient will be taken upon completion of surgery.
c. Operating room in which surgery will be done.
d. Induction room in which the patient will be anesthetized.
11. The specialist assigned to bring MSG Jackson to the surgical suite must obtain him from which place?
a. Recovery room.
b. Room one.
c. Emergency ward.
d. Nursing unit 16A.
12. What action should occur at 0730 hours?
a. Someone should go to the ward and bring the patient to the OR.
b. The scrub and the circulator should begin setting up the OR.
c. The anesthetist should begin the induction of anesthesia.
d. The surgeon should make the incision.
13. In accordance with the listing of the surgeons for MSG Jackson, the scrub must obtain whose suture card?
a. Only Dr. Croft’s.
b. Only Dr. Ferman’s.
c. Only Dr. Dudley’s
d. All of the above surgeons.
14. With the knowledge that the patient will have a right nephropexy. Which of the following does the specialist have the information to determine?
a. Sutures required.
b. Operative area.
c. Number of sterile gowns and gloves required.
d. Time the induction of anesthesia will begin.
15. What operative procedure do the surgeons plan to perform upon MSG Jackson’s right kidney?
a. Incision.
b. Excision.
c. Fixation.
d. Fusion.
16. The abbreviation “Endo” indicates that:
a. The patient will be examined with an endotracheal tube.
b. An endotracheal tube will be kept immediately available for emergency use.
c. An endotracheal tube will be placed in the patient’s trachea through his mouth or nose.
d. An endotracheal tube will be placed in the patient’s trachea through an incision in his throat.
17. Which of the following actions is appropriate for the circulator in assisting a member of anesthesiology service, MAJ Dodd?
a. Set up the anesthetist’s table.
b. Set up the gas anesthesia apparatus.
c. Place a revolving stool at the head of the operating table.
d. Set up cautery equipment.
18. Who makes the decision as to the scrub’s appropriate position at the operating table?
a. Dr. Croft.
b. Dr. Ferman.
c. SFC Clark.
d. SFC Good.
19. What does the “(S)” after SFC Good’s name mean?
a. He will supply the sutures needed for the case.
b, He will pour the required solutions.
c. He will stay in the room to help as needed.
d. He will serve as the senior scrub.
20. What does “T.1000 ml” indicate?
a. A tourniquet will be placed on the patient after he has lost 1000 ml of blood.
b. A tube (endotracheal) will be placed into the patient while the last 1000 ml of anesthetic is being given.
c. The patient will be given whole blood at 1000 hours.
d. The patient has been typed and cross-matched for 1000 ml of whole blood.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR EXERCISE 21. Exercise 21 is based on the second operation listed.
21. Since “TF” is entered on the operating room schedule, when should the scrub and the circulator prepare the operating room?
a. Twenty minutes after completion of the preceding case.
b. Immediately upon completion of the preceding case.
c. Twenty minutes before completion of the preceding case.
d. When setting up for the first case.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR EXERCISE 22. Exercise 22 is based on the fifth operation listed.
22. “Herniorrhaphy” means that a hernia will be surgically:
a. Drained.
b. Removed.
c. Repaired.
d. Injected.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR EXERCISE 23. Exercise 23 is based on the fourth operation listed.
23. Which of the following is a duty of the circulator with regard to the patient’s anesthetic?
a. Notify the anesthesiology service that the patient is to have local anesthesia.
b. See that a source of oxygen is available in the room.
c. Remind the surgeon to obtain a source of oxygen and place it in the room.
d. Set up the sterile table for the injection of the anesthetic.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR EXERCISES 24 AND 25. Exercises 24 and 25 are based on the last operation listed.
24. A hernioplasty is what kind of a surgical procedure?
a. Introduction.
b. Fixation.
c. Repair.
d. Crushing.
25. According to the anesthetic, the patient is scheduled to receive. Where should he be taken upon completion of surgery?
a. Ward 42B.
b. Recovery room.
c. Ward 16A.
d. Room IV.
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES, LESSON 2
1. d (para 2-b(1))
2. a (para 2-3a(3), d(1))
3. d (para 2-8e(1))
4. b (para 2-27b)
5. c (para 2-28b)
6. d (para 2-31c)
7. c (para 2-34e)
8. d (para 2-30)
9. a (para 2-33)
10. c (para 2-35b)
11. d (para 2-35f)
12. d (para 2-35c)
13. a (paras 2-35h, 2-35h(2))
14. b (paras 2-35g, 2-8e(1))
15. c (paras 2-8a(4), 2-8e(1))
16. c (para 2-35k)
17. c (para 2-35j)
18. d (para 2-35h(2), i)
19. d (para 2-35i)
20. d (para 2-35k(2))
21. b (para 2-35c)
22. c (para 2-10b)
23. b (para 2-35j)
24. c (paras 2-8a(1), b(4))
25. b (para 2-35f)
