2-25
2-25. WATER-SEAL CHEST DRAINAGE
a. General. Underwater-seal chest drainage is a closed (airtight) system for drainage of air and fluid from the chest cavity.
(1) The underwater-seal system is established by connecting a catheter (chest tube) that has been placed in the patient's pleural cavity to drainage tubing that leads to a sealed drainage bottle.
(2) Air and fluid drain into the bottle, but water acts as a seal to keep the air from being drawn back into the pleural space.
(3) By keeping the drainage bottle at floor level, fluid will be prevented from being siphoned back.
(4) As air and fluid are drained, pressure on the lungs is relieved and re-expansion of the lung is facilitated.
b. Selection of the System. The physician will specify the drainage setup he prefers to use. It is a nursing responsibility to be familiar with the various systems and their operation.
(1) When the physician specifies his preference, the nursing personnel will obtain, assemble, and check the system, maintaining asepsis within the system.
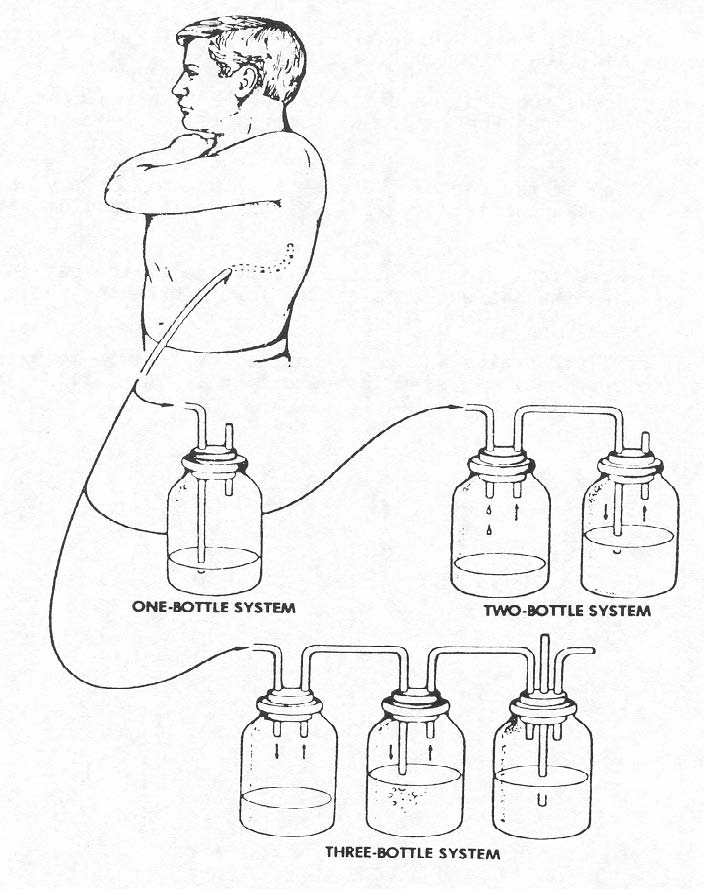
(2) Chest drainage can be organized into three types of systems. Each can be used with or without suction. Refer to Figure 2-2 as you read the descriptions that follow.
Figure 2-2. Water-seal drainage system
c. The Single-Bottle Water-Seal System.
(1) Connecting or drainage tubing joins the patient's chest tube with a drainage tube (glass rod) that enters the drainage bottle.
(2) The end of the glass rod is submerged in water, extending about 2.5 cm (1 inch) below the water level.
(3) The water seal permits drainage of air and fluid from the pleural space but does not allow air to reenter the chest.
(4) Drainage depends upon gravity, the mechanics of respiration, and, if ordered, the addition of controlled suction.
(5) The second tube in the drainage bottle is a vent for the escape of any air drained from the lung. If suction is ordered, it is attached here.
(6) Bubbling at the end of the drainage tube may or may not be visible. Bubbling may mean persistent air leaking from the lung or a leak in the system.
(7) The water level in the bottle fluctuates as the patient breathes. It rises when the patient inhales and lowers when the patient exhales.
(8) Since fluid drains into this bottle, be certain to mark the water level prior to opening the system to the patient. This will allow correct measurement of patient drainage.
d. The Two-Bottle Water-Seal System.
(1) The two-bottle system consists of the same water-seal bottle plus a fluid collection bottle.
(2) Pleural fluid accumulates in the collection bottle, and not in the water-seal bottle (as in the single-bottle system).
(3) Drainage depends upon gravity or the amount of suction added to the system.
(4) When suction is added, it is connected at the vent tube in the water-seal bottle.
e. The Three-Bottle Water-Seal System.
(1) This system consists of the water-seal bottle, the fluid collection bottle, and a third bottle which controls the amount of suction applied.
(2) The third bottle, called the manometer bottle, has three tubes. One short tube above the water level comes from the water-seal bottle. A second short tube leads to the suction. The third tube extends below the water level and opens to the atmosphere outside the bottle. It is this tube that regulates the suction, depending upon the depth the tube is submerged. It is normally submerged 20 cm (7.6 inches).
(3) The suction pressure causes outside air to be sucked into the system through the tube, creating a constant pressure. Bubbling in the manometer bottle indicates the system is functioning properly.
f. Commercial Systems.
There are several disposable commercial drainage systems available. They are plastic devices, divided into chambers for fluid collection, water-seal, and suction control. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for commercial drainage systems used at your facility.