Blood, Electrolytes, and Intravenous Infusions
2-6
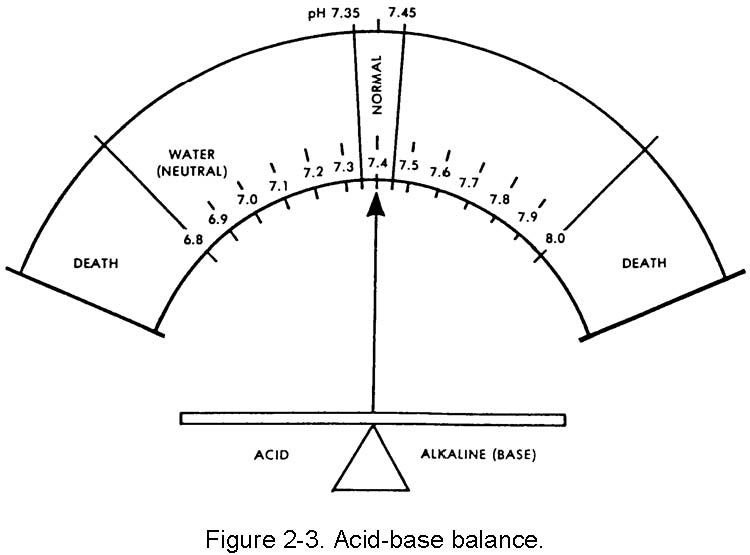
2-6. ACID-BASE BALANCE
The body's internal liquid environment is comprised of the body's fluids and the blood. For proper body functions to continue normally, this internal environment must be kept constant (homeostasis) and within a very narrow limit. The acid-base balance of the blood is maintained by the chemical balance between the
cations and the anions, which must be there in a very delicate balance. The cations are sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), calcium (Ca+2) and magnesium (Mg+2). The anions are chloride (Cl–), bicarbonate (HCO3–), phosphate (PO4–3), and sulfate (SO4–2). The acid-base balance is normally expressed as the "pH." This expression is a relationship of the hydrogen ion (acid) concentration in the blood (or in the body) and an arbitrary number. The balancing part (base or alkaline) is a hydroxy group (OH –). The normal range of the blood pH is 7.35 to 7.45. There is a daily variation caused by production of acids by exercise and metabolism of food. In the terminal stages of some diseases, pH can vary from a low of 6.8 to a high of 7.8. The concept of pH may be easier to understand by comparing the acid (hydrogen) and base (hydroxl) factors to pure water, which is neutral (neither acid nor base). The body is always slightly alkaline. The body's acid-base balance is effectively maintained under normal circumstances by the various buffer processes which neutralize strong acids or strong bases (alkalines) using the body's various buffer systems (chemical, organic, and so forth) to help excrete excess body system products. Figure 2-3 shows the narrow range of the body's pH.