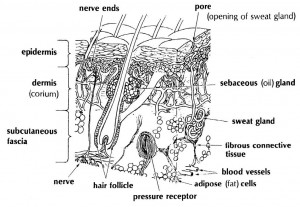
a. An intradermal (ID) injection is the injection of a small amount of fluid into the dermal layer of the skin (see figure 2-10).
It is frequently done as a diagnostic measure, such as for tuberculin testing (screening test for tuberculosis referred to as a tine test) and allergy testing (placing very small amounts of the suspected antigen or allergen in a solution under the skin).
[otw_is sidebar=otw-sidebar-1]
The intradermal injection is made in skin areas of the body that are soft and yielding.
b. Often the tuberculin syringe is the only syringe with fine enough calibrations to measure the minute dose that is used.
A 26-gauge needle, which is one-fourth to one-half inch in length, is usually selected. The fluid is in a small welt or “wheal” (a small swelling of the skin due to the medication placed under the skin) just under the surface of the skin and between its layers.