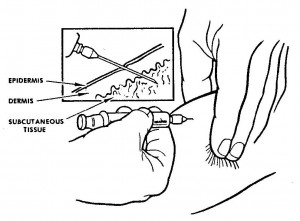
a. The subcutaneous (SQ) method of injection is commonly ordered for medication that requires a slower absorption rate than IM injections provide.
[otw_is sidebar=otw-sidebar-1]
b. The needle must pass through the epidermis and dermis to reach the subcutaneous fatty (adipose) tissue (see figure 2-7). Small volumes of medication that are voluble and nonirritating to body tissues are administered by this method. A variety of medications, such as insulin and some immunizations, are given subcutaneously.