a. The primary function of the urinary system is to control the composition, volume, and pressure of the body’s fluids by regulating excretion of water and solutes.
b. Circulating blood is filtered by the kidneys, where nonessential solutes are removed or “cleared” from the blood. Essential chemicals and water are restored to the blood in accordance with the body’s homeostatic requirements.
c. Metabolic waste products, foreign substances, and water are removed from the body in the form of urine.
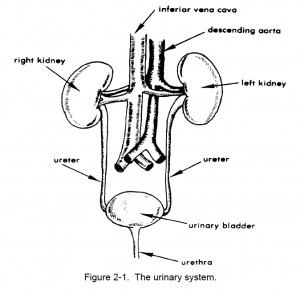
d. The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, one urinary bladder, and one urethra (figure 2-1).