a. Monitor the casualty’s breathing. Keep the airway open and perform rescue breathing or cardiopulmonary resuscitation, if needed.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is not indicated in the tactical situation when other casualties would benefit from treatment efforts. Insert a Combi-tube airway to protect the casualty’s airway.
b. Initiate an intravenous infusion, if needed.
c. Continue to check the casualty’s level of consciousness (AVPU or Glascow Coma Scale [GCS] method) and vital signs every 15 minutes. Observe for signs and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
d. Evacuate the casualty.
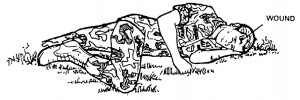
e. If you must leave the casualty, position him so he will not aspirate vomitus should vomiting occur. If the casualty is lying in a prone position, make sure his head is turned to one side. Otherwise, position the casualty on his side as shown in figure 5-1. Keep the casualty’s head, neck, and back in alignment when repositioning the casualty. Place padding such as a rolled poncho or a folded field jacket around the casualty to support the casualty and maintain spinal alignment.