You must also act to keep the enemy from gaining information about US
operations. That action, called counterintelligence, involves:
Commanders get information from many agencies, but you are their best
agency. You can collect information from the following sources:
-
Prisoners of war (PW)
are an immediate source of information. Turn
captured soldiers over to your leader quickly. Also, tell him anything you
learn from them.
-
Captured documents
may contain valuable information about present or
future enemy operations. Give such documents to your leader quickly.
-
Enemy activity
(the things the enemy is doing) often indicates what he
is going to do. Report everything you see the enemy do. Some things that may
not seem important to you may be important to your commander.
-
Local civilians
often have information about the enemy, terrain, and
weather in an area. Report any information gained from civilians. However, you
cannot be sure which side the civilians are trying to help, so be careful when
acting on information obtained from them. Try to confirm that information by
some other means.
WHAT TO REPORT
Report all information about the enemy to your leader quickly, accurately,
and completely. Such reports should answer the questions WHO? WHAT? WHERE? after
"WHEN?" It is best to use the "SALUTE" format (size, activity, location, unit,
time, and equipment) when reporting. To help you remember details, make notes
and draw sketches.

Size. Report the number of soldiers and vehicles you saw. For
example, report '' 10 enemy infantrymen" (not "a rifle squad") or '' 3 enemy
tanks" (not "an enemy tank platoon").
Activity. Report what you saw the enemy doing. For example,
"emplacing mines in the road."
Location. Report where you saw the enemy. If you have a map, try to
give an eight-digit coordinate, such as "GL 874461." If you do not have a map,
relate the location to some key terrain, such as "on the Harm Road, 300 meters
south of the Ken River Bridge."
Unit. Report the enemy's unit. If the unit is not known, report any
distinctive features, such as bumper markings on trucks, or type of headgear.
Some armies have distinctive uniforms and headgear, or colored tabs on their
uniforms, to identify types of units. A unit's action may also indicate its
type. The kind of equipment observed may be peculiar to a certain type of unit.
For example, a BRDM may indicate a reconnaissance unit.
Time. Report the time you saw the enemy activity, not the time you
report it. Always report local or Zulu (Z) time.
Equipment. Report all of the equipment the enemy is wearing or using.
If you do not recognize an item of equipment or a type of vehicle, sketch it and
submit the sketch with the report. The following is an example of a SALUTE
report.
FM: 1st Plt, C Co, 2d Bn, 1/73 Inf.
TO S2, 2d Bn, 1/73
Inf.
Combat OP sighted four enemy tanks moving west along secondary road at grid
coordinates NB613397 at 241730Z. Tanks traveling at approximately 5 kilometers
per hour. Hatches were open and visible enemy personnel were wearing protective
masks.
PRISONERS OF WAR AND CAPTURED DOCUMENTS
PWs are a good source of information. They must be handled without breaking
international law and without losing a chance to gain intelligence.
Treat PWs humanely. Do not harm them, either physically or mentally. The
senior soldier present is responsible for their care. If PWs cannot be evacuated
in a reasonable time, give them food, water, and first aid. Do not give them
cigarettes, candy, or other comfort items. PWs who receive favors or are
mistreated are poor interrogation subjects.
HANDLING PWs
In handling PWs, follow the five S's:
1. Search PWs as soon as they are captured. Take their weapons and
papers, except identification papers and protective masks. Give them a written
receipt for any personal property and documents taken. Tag documents and
personal property to show which PW had them.
When searching a PW, have one man guard him while another searches him. (A
searcher must not get between a PW and the guard.) To search a PW, have him
spread-eagle against a tree or wall, or get into a pushup position with his
knees on the ground. Search him, his equipment, his clothing.

2. Segregate PWs into groups by sex and into subgroups such as enlisted
personnel, civilians, and political figures. This keeps the leaders from
promoting escape efforts. Keep the groups segregated as you move them to the
rear.
3. Silence PWs and do not let them talk to each other. This keeps them
from planning escape and cautioning each other on security. Report anything a PW
says or does.
4. Speed PWs to the rear. Turn them over to your leader. He will assemble
them and move them to the rear for questioning by the S2.
5. Safeguard PWs when taking them to the rear. Do not let anyone abuse
them. Watch out for escape attempts. Do not let PWs bunch up, spread out too
far, or start diversions. Such conditions may create a chance for escape.
If a PW is wounded and cannot be evacuated through normal channels, turn him
over to an aidman to be evacuated through medical channels.
Before evacuating a PW, attach a tag to him. You can make these tags
yourself. The format for the tags is given in the following illustration.
The battalion S2 should be able to supply these tags.
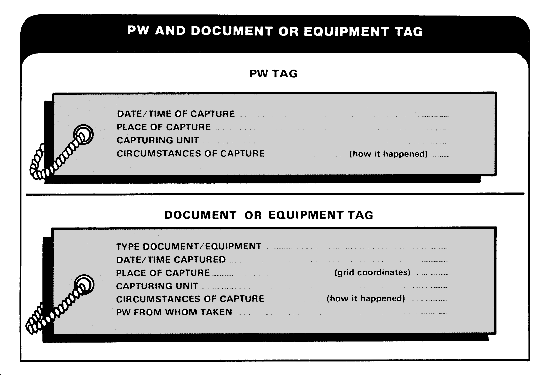
HANDLING CAPTURED DOCUMENTS AND EQUIPMENT
Enemy documents and equipment are good sources of information. Documents may
be official (maps, orders, records, photos) or personal (letters or diaries).
If such items are not handled properly, the information in them may become
lost or outdated. Give them to your leader quickly. Tag each item using the form
shown above. If the item was found on a PW, put that PW's name on the tag.
COUNTERINTELLIGENCE MEASURES
The enemy must not get information about US operations. This means that you
and your fellow soldiers must:
-
Practice camouflage principles and techniques.
-
Practice noise and light discipline.
-
Practice field sanitation.
-
Use proper radiotelephone procedure.
-
Use the challenge and password properly.
-
Not take personal letters or pictures into combat areas.
-
Not keep diaries in combat areas.
-
Be careful when discussing military affairs (the enemy may be listening).
-
Use only authorized codes.
-
Abide by the Code of Conduct (if captured).
-
Report any soldier or civilian who is believed to be serving or
sympathetic with the enemy.
-
Report anyone who tries to get information about US operations.
-
Destroy all maps or important documents if capture is imminent.
-
Not discuss military operations in public areas.
-
Discuss military operations only with those persons having a need to know
the information.
-
Remind fellow soldiers of their counterintelligence responsibilities.





