a. Definition.
Episiotomy is an incision into the perineum made to facilitate delivery.
b. Types of Episiotomies
(1) Median or midline episiotomy. An incision is made in the midline of the perineum. The advantages of a median or midline episiotomy are that they are easy to repair, faulty healing is rare, there is less pain during the postpartal period, there is less blood loss, and the anatomic end results almost always excellent.
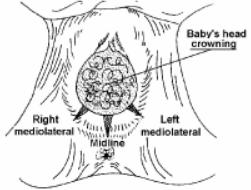
(2) Mediolateral episiotomy. An incision is made in the midline but directed to the right or left. The advantages of a mediolateral episiotomy are that there is less tearing beyond the incision and the incision can be directed away from the rectum. The disadvantages are that there is greater blood loss, faulty healing is more common, there is more perineal discomfort, and they are more difficult to repair.
c. Reasons for Episiotomy.
An episiotomy results in a clean surgical cut instead of a ragged tear, it minimizes pressure on the fetal head, and shortens the second stage of labor.
d. Repair.
The obstetrician sutures the cut after delivery of the fetus and the placenta. There is usually slight blood loss because pressure of the presenting part constricts the cut edges and keeps bleeding to a minimum.
e. Nursing Intervention.
(1) Observe incision for signs of infection (for example, redness, swelling, unusual discharge).
(2) Instruct the patient to change her perineal pad each time she uses the toilet.
(3) Teach the mother to do perineal cleansing each time she uses the bathroom.
(4) Assist the mother to use the Sitz bath as ordered.
(5) Use a perineal lamp (usually a gooseneck lamp) to improve circulation, promote healing, and ease discomfort. The lamp should not be used too early, otherwise bleeding may occur. Wait about 12 hours after delivery. The lamp should be placed no less than 18 inches from the perineum. Use a 25 to 40 watt bulb. The lamp can be used several times a day for 20-minute intervals. Drape the patient legs to provide maximum privacy.
(6) Offer local anesthetics (nupercainal ointment, tucks, witch hazel compresses) as ordered.
