This is the Archived Desktop Edition.
You should be transferred to the Newest Edition for Desktop and Mobile within 2 seconds.
![]()
Multimedia Edition
|
Self-Test Lesson 1 Exercises
EXERCISES, LESSON 1
INSTRUCTIONS: Complete the following exercises by marking the lettered response that best answers the question, by completing the incomplete statement, or by writing the answer in the space(s) provided.
After you have completed all of these exercises, turn to "Solutions to Exercises" at the end of the lesson and check your answers. For each exercise answered incorrectly, reread the material referenced with the solution.
1. List the female's internal reproductive organs.
________________________. _______________________.
________________________. _______________________.
2. The _______________ is suspended by broad ligaments and is located between the urinary bladder and the rectum.
3. The ________________ provides the passageway for childbirth and menstrual flow.
4. The female has ____fallopian tubes.
a. Two.
b. Three.
c. Four.
5. Which of the female reproductive organs has finger-like projections that partially surround each ovary?
_______________________________________________.
6. ______________ are for the production of oogenesis and hormones.
7. ___________________ works with estrogen to produce a normal menstrual cycle.
8. Vaginal introitus is known as the _________________________.
9. Days 6-14 of the hormonal interaction of the female cycle is known as the
__________________ phase.
10. What is the name of the male's sex hormone?
__________________.
11. What male reproductive organ is suspended in the scrotal sac outside of the abdominopelvic cavity?
__________________
12. The __________________ caps the superior part of the testes and runs down its posterior side.
13. The male's accessory glandular structure includes:
________________________. _______________________.
________________________. _______________________.
14. The _______________ is anterior to the head of the mature sperm.
15. The male's interstitial cells are activated during puberty by two hormones,
__________ and ___________.
Special Instructions for Exercises 16 Through 32. Match the information in Column A with the appropriate word or term in Column B. Place the letter of the response in the blank space at the left of the number in Column A.
|
COLUMN A _____16. Upon dividing 2 different cells are produced, each containing 23 chromosomes. _____17. Menopause. _____18. Transport ovum from the ovaries to the uterus. _____19 . Epididymis and vas deferens. _____20 . Corpus, fundus, cervix, isthmus. _____21. Pouches that store sperm. _____22. Ovaries, uterus, vagina, fallopian tubes. _____23. Cowper's glands, penis, prostate, seminal vesicles. _____24. Tail, midpiece, head. _____25. Mons pubis, vestibule, perineum, Bartholin's glands. _____26. Menses phase, proliferative phase, secretory phase. _____27. Peritoneum, myometrium, endometrium. _____28. Millions of sperms produced in the seminiferous tubules. _____29. Controlled by the cyclic activity of FSH and LH. _____30. Produces female sex eggs, estrogen, and progesterone. _____31. Testes. _____32. Clitoris, urethral meatus, vaginal introitus. |
COLUMN B a. internal b. walls of the uterus c. ovaries d. divisions of the uterus e. external female organs f. menstrual cycle g. fallopian tubes h. primary oocyte i. hormonal interaction ofthe female cycle j. menstruation cessation k. produces sperm and testosterone l. male's duct system m. vestibule n. accessory glandular structure o. seminal vesicles p. spermatogenesis q. regions of a mature sperm |
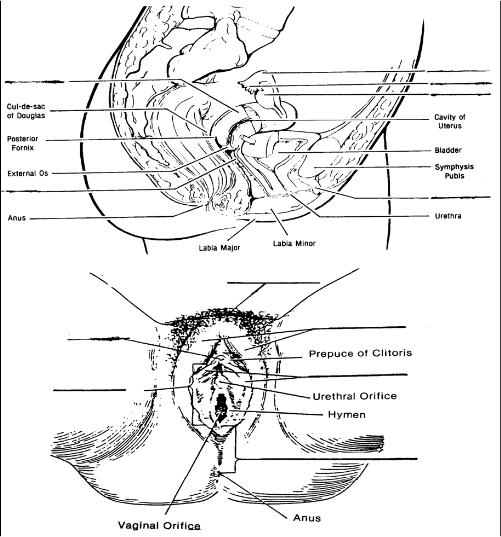
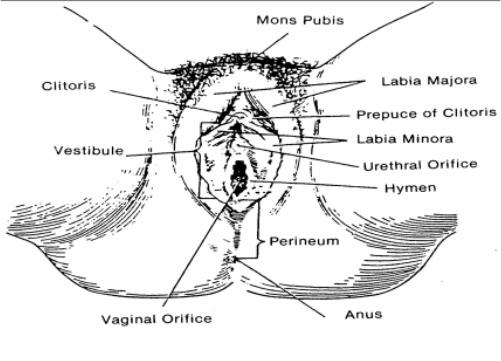
33. Identify each of the parts indicated in the drawings of the female's reproductive system below.
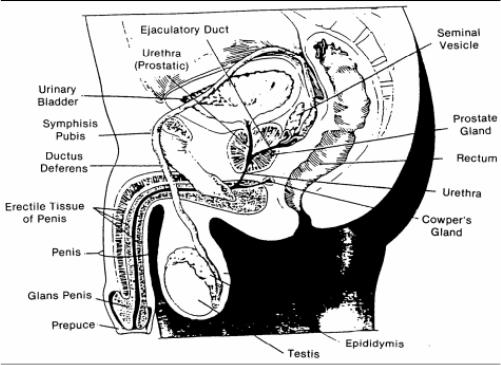
34. Identify each of the parts indicated in the drawing of the male's reproductive system below.
Check Your Answers
SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES, LESSON 1
1. uterus.
vagina.
fallopian tubes.
ovaries (para 1-3).
2. uterus (para 1-3a(1)).
3. vagina (para 1-3b(2)).
4. a (para 1-3c).
5. fallopian tubes (para 1-3c(3)).
6. Ovaries (para 1-3d(1)).
7. Progesterone (para 1-3d(4)(b)).
8. vaginal entrance (para 1-4d(3)).
9. proliferative (para 1-6b(2)).
10. testosterone (para 1-9).
11. testes (para 1-10a).
12. epididymis (para 1-10b(1)).
13. seminal
vesicles.
prostate gland.
Cowper's gland.
penis (para 1-10c).
14. acrosome (para 1-11f).
15. FSH and LH (para 1-12)
16. h (para 1-3d(3)(c)).
17. j (para 1-8).
18. g (para 1-3c(2)).
19. l (para 1-10b).
20. d (para 1-3a(2)).
21. o (para 1-10c(1)).
22. a (para 1-3).
23. n (para 1-10c).
24. q (para 1-11e).
25. e (para 1-4).
26. I (para 1-6b).
27. b (para 1-3a(3)).
28. p (para 1-11b).
29. f (para 1-6a).
30. c (para 1-3d(1)).
31. k (para 1-10a).
32. m (para 1-4d).
33. Solution for exercise #33 (female's reproductive organs).
_500.jpg)
34. Solution for exercise number 34 (male's reproductive organs).
End of Lesson 1
|
|
|||||||||
|