|
Pneumonia (consolidation)
Infection of the air spaces (air
bronchograms) and/or interstitium of the lung.
Finding:
-
Depending upon the amount and
distribution of the airspaces involved, this may present as confluent
parenchymal (lobar or segmental) opacity or merely patchy opacity.
-
If the Interstitium is
predominantly involved, it may appear as a reticulonodular pattern.
-
Air bronchograms would confirm an
alveolar process.
-
The lung volume should not be
lost (may even be increased).
-
Usually all radiographic
abnormalities should disappear after 6 weeks of appropriate antibiotic
therapy. However, pneumonia may
be complicated by abscess or empyema formation.
Examples of Pneumonias and how to
determine location. (look for the silhouette sign…loss of usual visualized
borders.)
Consolidation Pattern
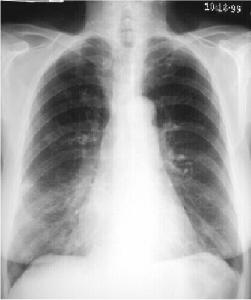
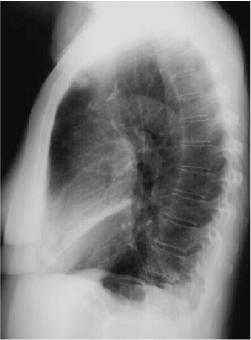
Right Middle Lobe Consolidation
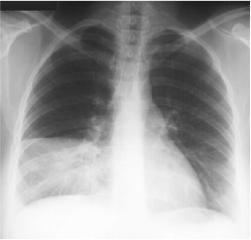
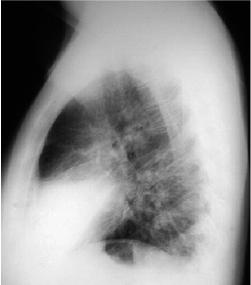
Right Middle Lobe Pneumonia
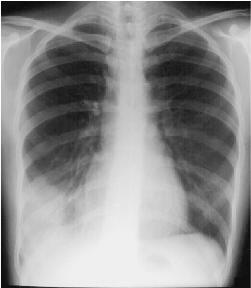
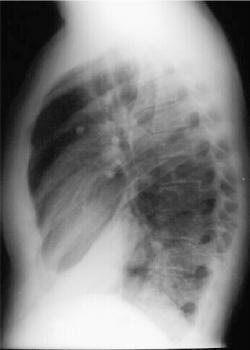
Right Lower Lobe Pneumonia


Right Lower Lobe Pneumonia, Anterior Segment
|
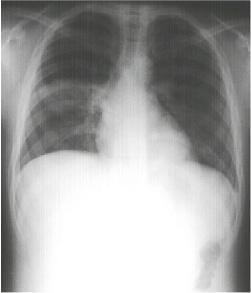
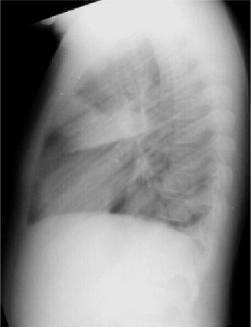
Right Lower Lobe Pneumonia, Superior Segment
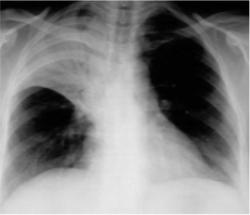
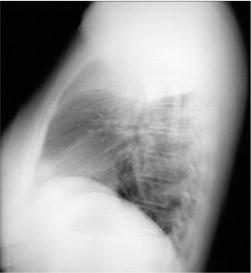
Right Upper Lobe Pneumonia
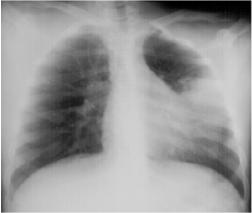
Left Lingular Pneumonia
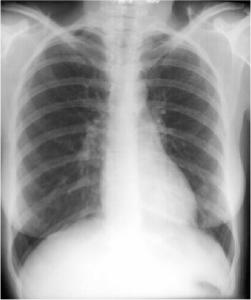
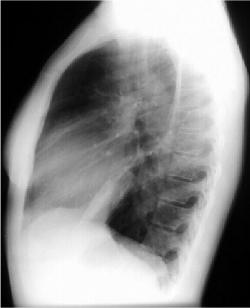
Left Lower Lobe Pneumonia, Anterior Segment
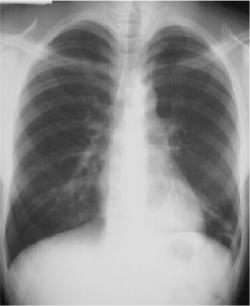
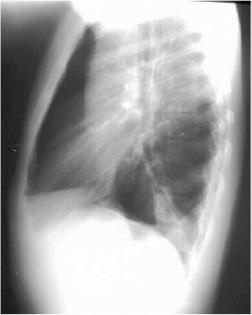
Left Lower Lobe Pneumonia, Posterior Segment
Round Pneumonia
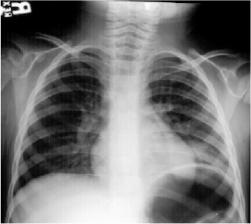
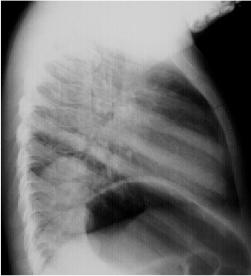
Round Pneumonia
Round Pneumonias are found typically in the
child. Most often the organism is pneumococcus. The pneumonia appears round because
of poorly developed collateral pathways (pores of Kohn and channels of Lambert).
Over time though initially round, it develops into a more consolidative
pattern.
This section written by:
LCDR Ron Boucher, MC, USN
LT Hugh McSwain, MC, USN
With some assistance from:
CDR Michael Puckett, MC, USN
ENS Robert Post, MC, USNR
|