|
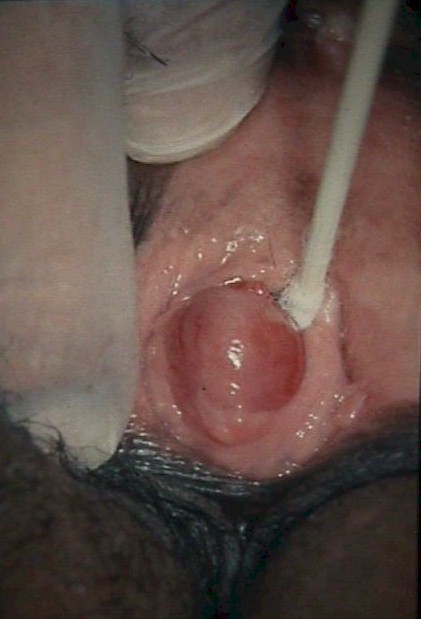
A Skene's gland is on each side of the urethral opening. It is normally
neither seen nor felt, although close inspection will reveal the pinpoint openings of
these periurethral glands.
When infected, the Skene's gland will become enlarged and tender.
A simple incision and drainage of the gland will generally result in complete
resolution. Topical anesthetic (20% benzocaine, or "Hurricaine") can be applied
to the cyst with a cotton-tipped applicator and allowed to sit for 3-4 minutes. A
single stab wound by a scalpel opens the abscess and allows for drainage of the pus.
Cultures, particularly for gonorrhea, should be obtained.
 Good choices for antibiotics would
include those most helpful for treating urethritis: Good choices for antibiotics would
include those most helpful for treating urethritis:
-
Cefixime 400 mg orally in a single dose, OR
-
Ceftriaxone 125 mg IM in a single dose, OR
-
Ciprofloxacin 500 mg orally in a single dose, OR
-
Ofloxacin 400 mg orally in a single dose,
PLUS
 |
|