Contents · Introduction · Learning Objectives · Textbook · Lectures · Procedures · Final Exam · Library · Laboratory · Pharmacy · Imaging · Forms · Videos · About · Contact Us>
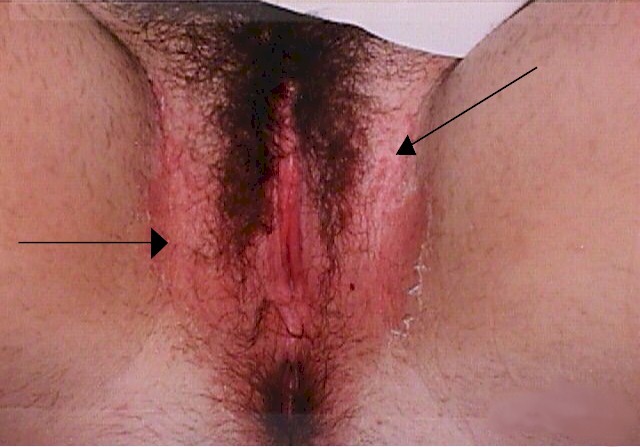
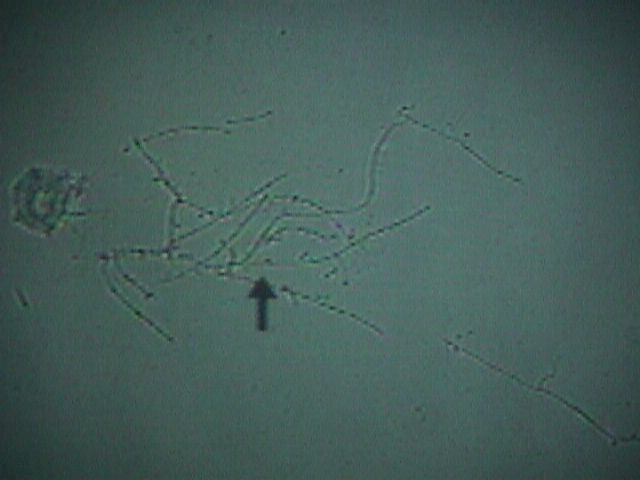
YeastVaginal yeast infections are common, monilial overgrowths in the vagina and vulvar areas, characterized by itching,dryness, and a thick, cottage-cheese appearing vaginal discharge. The vulva may be reddened and irritated to the point of tenderness. Yeast thrives in damp, hot environments and women in such circumstances are predisposed toward these infections.Women who take broad-spectrum antibiotics are also predisposed towards these infections because of loss of the normal vaginal bacterial flora. Yeast organisms are normally present in most vaginas, but in small numbers. A yeast infection, then, is not merely the presence of yeast, but the concentration of yeast in such large numbers as to cause the typical symptoms of itching, burning and discharge. Likewise, a "cure" doesn't mean eradication of all yeast organisms from the vagina. Even if eradicated, they would soon be back because that is where they normally live. A cure means that the concentration of yeast has been restored to normal and symptoms have resolved. The diagnosis is often made by history alone, and enhanced by the classical appearance of a dry, cheesy vaginal discharge. It can be confirmed by microscopic visualization of clusters of thread-like, branching Monilia organisms when the discharge is mixed with KOH. Recommended Regimens (CDC 2002) Intravaginal Agents:
Reoccurrences are common and can be treated the same as for initial infections. For chronic recurrences, many patients find the use of a single applicator of Monistat 7 at the onset of itching will abort the attack completely. Sexual partners need not be treated unless they are symptomatic.
|
This information is provided by The Brookside Associates. The Brookside Associates, LLC. is a private organization, not affiliated with any governmental agency. The opinions presented here are those of the author and do not necessarily represent the opinions of the Brookside Associates or the Department of Defense. The presence of any advertising on these pages does not constitute an endorsement of that product or service by either the US Department of Defense or the Brookside Associates. All material presented here is unclassified.
C. 2009, 2014, All Rights Reserved